The evolution of risks faced by modern organizations demands the adoption of flexible, scalable, and innovative solutions. User-managed intelligent automation is one such solution used to mitigate these risks efficiently and cost-effectively.
With the internal audit function already juggling multiple responsibilities to address the current risk universe, attempting to transform for greater readiness and strategic enterprise input can be a challenging endeavor.
Enter automation.
Why Automate Within Internal Audit
When deployed and governed effectively, automation can help solve many of the common challenges internal auditors face daily.
In a recent webinar of 1,000+ internal audit, technology, and risk management professionals conducted jointly with AuditBoard, nearly 50% of attendees noted they experience all the following four challenges commonly solved by intelligent automation and data analytics:
- Regulatory requirements: Annual compliance requirements (SOX, NIST, PCI-DSS) are often clearly defined and repetitive, making them perfect candidates for automation.
- Budget constraints: Smaller internal audit teams with fewer resources can more effectively execute audit plans with the aid of automation, which, over time, can have less of a budget impact than hiring additional staff or outsourcing to a third party.
- Rapidly evolving risks: New risks present new challenges but also opportunities for transformative risk management. Cybersecurity and data privacy risks, for instance, already prompt internal auditors to think differently about risk mitigation practices and strategies. The use of automation can further shape and adapt the internal audit function, allowing risk teams to be more dynamic and data-driven while conquering compliance and proactively anticipating emerging risks.
- Employee focus: Teams with more time to work on stimulating and strategic tasks tend to have increased satisfaction within their roles. Automation can accelerate the transition to these kinds of activities while also reducing the cost of training and onboarding new resources. Additionally, automation helps teams avoid burnout commonly caused by document request delays and the monotony of completing routine tasks and testing procedures.
Getting Started: Align on Strategic Priorities
Before embracing intelligent automation, internal audit teams should hold frank discussions with relevant business functions and organizational leaders. It’s important to ensure automation aligns with the future vision of the company and directly addresses core challenge areas while gaining appropriate buy-in at key levels.
By prioritizing the automation opportunities that directly support top priorities, internal audit can draw a straight line between their actions and investments to tangible results supporting the long-term strategic goals of the company.
At this juncture, it’s also key to have a long-term, holistic perspective on the adoption of automation tools. As is the case with other technologies, scalability matters. The automation platforms, and the process architecture built around them, can have greater impact and strategic advantage when they can also serve other teams, functions, and organizational priorities beyond the four walls of internal audit.
In this way, a collaborative, effective partnership with non-internal audit decision-makers can expedite automation investments and reduce time-to-adoption and time-to-ROI.
Explore expert Risk Management solutions that solve real-world problems
Increase the value of internal audit and transform your enterprise risk function holistically to stay ahead of new standards, complexities, technologies, and threats.
How to Find Priority Automation Opportunities for Internal Audit
To justify the efficacy and value in rolling out automation platforms within internal audit, it’s important to understand the potential scope of the automation program and, critically, where it can drive significant business impact and success.
To identify these key opportunities, consider the approach below:
- Analyze current manual processes to identify suitable automation candidates (commonly manually time-intensive processes and/or prone to human error).
- Define and document key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help measure the success of automation. KPIs can quantify efficiency, accuracy, and improvements to audit processes.
- Determine the specific application and fit of different software tools for automating the listed audit tasks.
- Conduct a cost-benefit analysis:
- Perform a cost-benefit analysis on each potential automation project.
- Quantify expected cost savings in terms of FTE hours savings, error-rate reduction, etc.
- Also note the qualitative benefits of automation, such as employee satisfaction and opportunities to reallocate resources to other high-value-added tasks or processes.
Areas where automation is commonly applied across each phase of the internal audit lifecycle include:
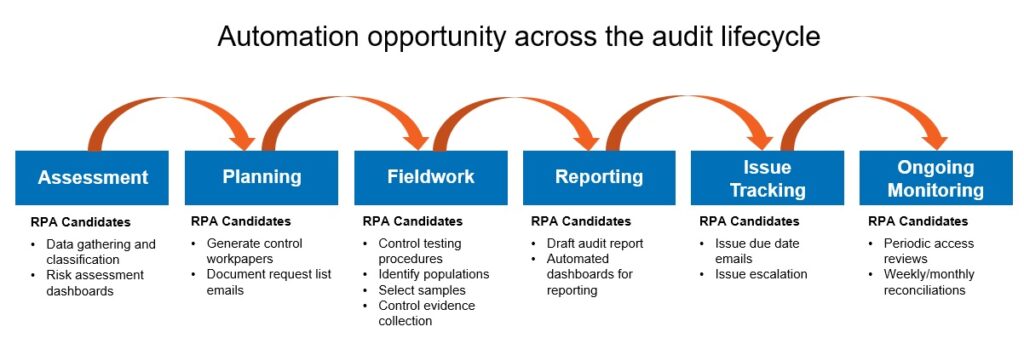
Deliver Better Automation Results With a Unique Approach
Automation is never one-size-fits-all. To maximize the value of automation (whether it’s process automation, intelligent workflow management, or even artificial intelligence-enabled automation), it must be designed, developed, and deployed for the specific needs of the internal audit function.
Specific ways to tailor automation and ensure a successful integration include:
- Strengthening data foundations: Access to structured, high-quality data from a robust, modern data architecture is a significant accelerator of automation.
- Creating standardized templates: A consistent, comprehensive approach to capturing information can create opportunities for reusable automation workflows.
- Building use-case libraries: Set up a basic intake process where team members can submit ideas and track items from ideation to approval to implementation.
- Engaging leadership: Include executive leadership and sponsors in ideation sessions and use-case reviews to directly expose them to automation and its transformative impact.
- Promoting an automation-first mindset: Encourage internal audit to continuously look out for new automation opportunities that improve efficiency and reduce risk.
- Establishing change management processes: Develop and adopt a standardized change management framework to ensure complete and accurate integration of automated tasks and compliance with corporate policies.
To take the next step in your automation journey, contact CrossCountry Consulting.
