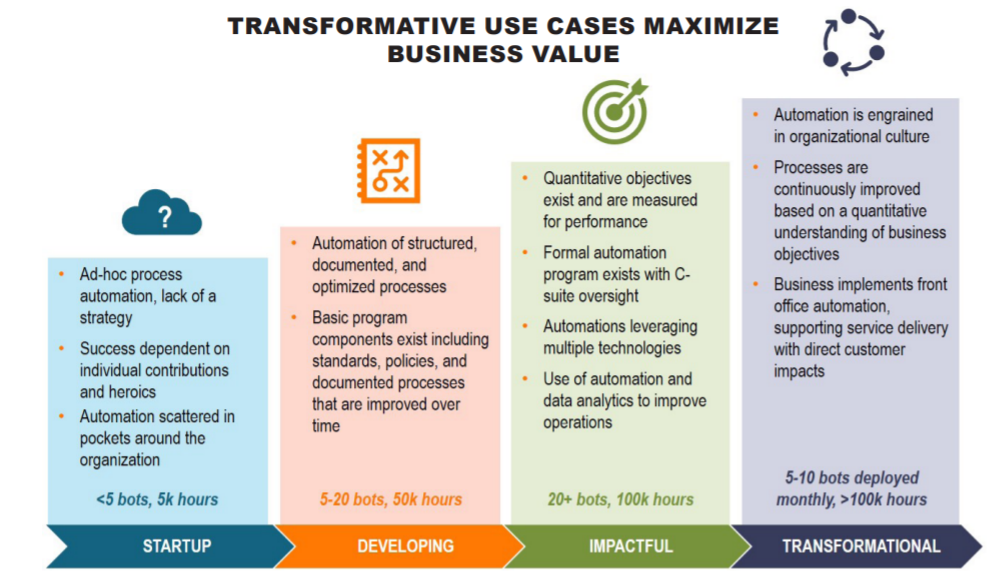
As businesses shift to decentralized work and a digital workforce, employees are being asked to complete more tactical roles and take on additional responsibilities.
To alleviate the growing mountain of tasks and influx on their employees’ time, companies are now considering new technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA). RPA software can totally reimagine the productivity and efficiency of a scaling organization, but it can simultaneously impact security risk.
Cyber Considerations With RPA
Amid a swell of digital transformation initiatives led by the deployment of software robots, cybersecurity can easily go overlooked.
But cybersecurity must be factored into the earliest stages of the implementation of an RPA tool. If not baked into the first phases of design, the RPA implementation can unknowingly create new threat and attack vectors for hackers and cybercriminals to exploit.
Nonetheless, robotics and cybersecurity can greatly complement one another, generating a greater level of risk awareness, security automation, and data security.
Leading automation platforms like UiPath come with essential cybersecurity functionality, including credential vaults, centralized logging, and access monitoring. Integrating with IT and cybersecurity processes and platforms that already exist within the organization can make implementations even more secure.
Below we describe critical security control risks inherent in an environment of unsecured RPA and bot processes. Then we detail how cyber hygiene best practices and key cybersecurity automation technology can manage these risks.
Elevated Access Privileges to Sensitive Data Sources
Business Risks
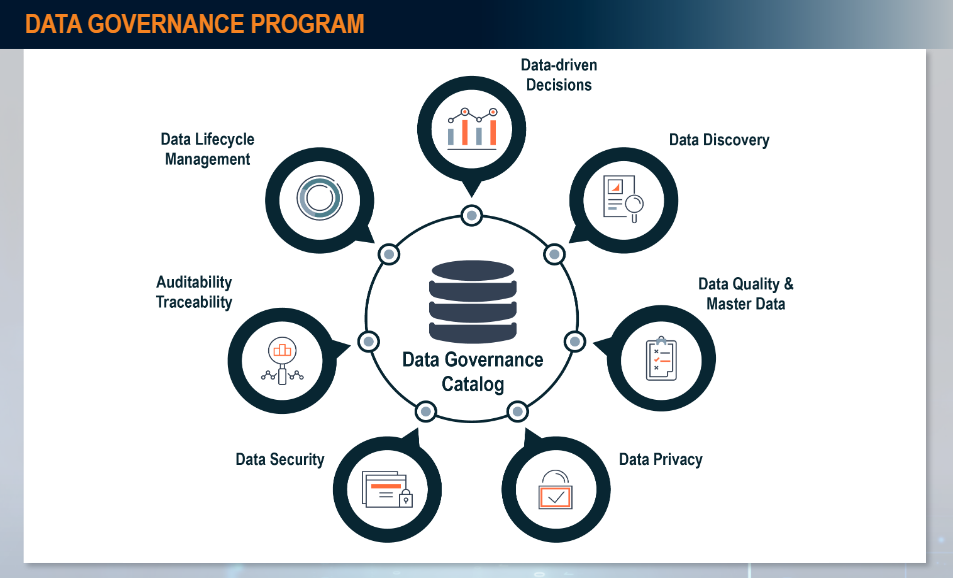
To automate processes that are well-suited to RPA, bots often require elevated access privileges to an organization’s data sources: the proverbial crown jewels. When provisioned inappropriately or misused, this access can open the door to the manipulation and export of sensitive data, which greatly damages confidentiality and integrity.
Cybersecurity Risk Management Techniques
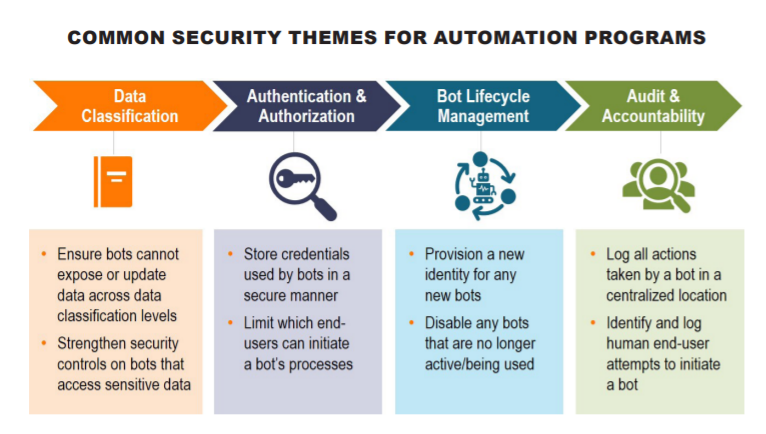
- Manage bot credentials in an enterprise credential vault (e.g., CyberArk or Centrify) to leverage existing access controls and certification mechanisms while limiting human accessibility and visibility to the password. This will jointly reduce human error and RPA bot failure.
- Assign unique credentials to each bot and ensure a human owner or manager is identified for each. Empowering specific human oversight of a software bot will enable the business to quickly remediate unauthorized access to sensitive information, ensure stronger compliance to process, and maintain data integrity.
- Consider the principles of least privilege and segregation of duties when provisioning access to a bot.
Logging & Monitoring of Bot Activities
Business Risks
Unattended bots allow for repetitive business processes (such as financial close processing) to be automated, freeing up employees’ time for more valuable tasks. If activity by an unattended bot is not logged and correlated against enterprise logs, a significant threat vector is exposed without the means to identify warning signs of bot misuse or a coordinated attack against the enterprise.
Any variance in behavior by unattended bots must be identified in a timely manner and tracked back to the specific bot.
Cybersecurity Risk Management Techniques
- Ensure logs from UiPath Orchestrator are fed into the centralized Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM) platform.
- Create detailed process design documentation for each automation. This will allow the Cybersecurity Operations Center (SOC) to create rules for alerting and tuning to ensure that variances from expected activity are identified and alerted.
- To decrease threat vectors for attackers, decommission bots by following established change management processes once an automation is no longer a required business process.
Proliferation of Access
Business Risks
The automation of central processes implies that multiple team members might need access to execute bots, which could result in staff being newly granted access to systems. Without careful monitoring, granted access could rise well above what is needed to perform their defined job responsibilities and steer away from following a least privileged access mindset.
Cybersecurity Risk Management Techniques
- Incorporate the granting a team member access to bots into recurring access certification campaigns to ensure unintended access is not granted through the use of a bot.
- To complete the process defined in the design documentation, ensure bots are designed to require only the minimum access required to different interfaces and applications.
- Consider the use of unintended automations to minimize interactions between team members and application interfaces.
- Reduce the likelihood of unintended exposure to sensitive data elements.
Organizational RPA Security at Scale
To ensure that you maintain a balanced approach that enables both automation and cybersecurity, it is critical to collaborate with your cybersecurity team during design, development, review, and deployment of your RPA program.
Interested in learning more about how to grow and scale your organization’s RPA program?
Download our guidebook about establishing a Robotic Operating Center of Excellence for an insight on why a COE matters, the steps and key considerations necessary to establishing a world-class program, and how to maximize your business value.
Editor’s note: Updated February 2022